重读 Swift (5.0) 第一篇
The Basics
1. Int
跟系统的 word size 相同,在32位系统上相当于Int32,在64位系统上相当于Int64。
如果没有特殊需求应该统一使用Int类型,而不是指定长度的Int类型。保持代码的一致和协同。
2. UInt
跟系统的 word size 相同,在32位系统上相当于 UInt32,在64位系统上相当于 UInt64 。
如果没有特殊需求,应该使用Int类型,即使明确知道存储的数据是非负的。统一使用Int类型,可以保持代码的一致和协同,方便类型推测,减少不必要的类型转换。
Int is preferred
3. Floating-Point Numbers
-
Double 表示64-bit 的浮点数
-
Float 表示32-bit 的浮点数 根据实际情况和要存储的数值范围选择合适的类型。
Double is preferred
4. Numeric Literals
以下都会识别为 Int 类型
- 十进制
let decimalInteger = 17 - 二进制
let binaryInteger = 0b10001 - 八进制
let octalInteger = 0o21 - 十六进制
let hexadecimalInteger = ox11
以下都会识别为Double类型
-
十进制 乘以 $10^{exp}$, 十进制浮点型的 exponent可选
- $1.25e2 = 1.25 \times 10^2 = 125.0$
- $1.25e-2 = 1.25 \times 10^{-2} = 0.0125$
-
十六进制 乘以 $2^{exp}$, 十六进制浮点型的 exponent不可省略
- 0xFp2 = $15 \times 2^2 = 60.0$
- oxFp-2 = $15 \times 2^{-2} = 3.75$
// Double 类型的12.1875表示 let decimalDouble = 12.1875 let exponentDouble = 1.21875e1 let hexadecimalDouble = 0xC.3p0
Basic Operators
1. Compound Assignment Operators
组合运算符(eg: +=)将连个运算同时计算
The expression a += 2 is shorthand for a = a + 2. Effectively, the addition and the assignment are combined into one operator that performs both tasks at the same time.
2. 比较运算符
tuple比较顺序是左到右依次比较,前面相等才比较后面的。
swift 标准库中只实现小于7位长的tuple的比较,更多位的比较需要自己实现比较运算符
3. Nil-Coalescing Operator
// 当a有值的时候b不会执行
a ?? b
4. R ange Operators
| a…b | a..<b | |
|---|---|---|
| a < b | fatalError | fatalError |
| a = b | 1 item | empty |
| a > b | b-a+1 items | b-a items |
在数组中的用法
let arr = ["a", "b", "c", "d"]
arr[2...] // ["c", "d"]
arr[...2] // ["a", "b", "c"]
arr[..<2] // ["a", "b"]
在迭代中的用法
-
省略第一个值 不可以迭代
-
省略最后一个值可以迭代,无穷迭代
-
可以一个one-side range是否包含某个值,如:
let range = ...5 range.containts(7) // false range.containts(4) // true range.containts(-1) // true
5. Logic Operators
swift 中逻辑运算符为左结合,从左到右执行,遵循short-circuit evaluation
Strings and Characters
1. 多行String
添加额外空格,与 closing “”” 对齐之前的空格不会带入只中
let linesWithIndentation = """
This line doesn't begin with whitespace.
This line begins with four spaces.
This line doesn't begin with whitespace.
"""
2. Extended Grapheme Clusters
-
String 会把多个可以连接的Unicode字符组合在一起
- count的计算为组合之后的值,所以count计算的时间复杂度应该是O(n)
- 当比较相等的时候也是通过组合之后的值进行比较
var word = "cafe"
print("the number of characters in \(word) is \(word.count)")
// Prints "the number of characters in cafe is 4"
word += "\u{301}" // COMBINING ACUTE ACCENT, U+0301
print("the number of characters in \(word) is \(word.count)")
// Prints "the number of characters in café is 4”
3. Substrings
-
substring 可以与原始string或者其他的substring共享内存。
-
substring不适合长时间的存储,因为它与原始string的内存共享,所以必须要求原始string存在与内存中。
Collection Types
1. Set
Fundamental Set Operations
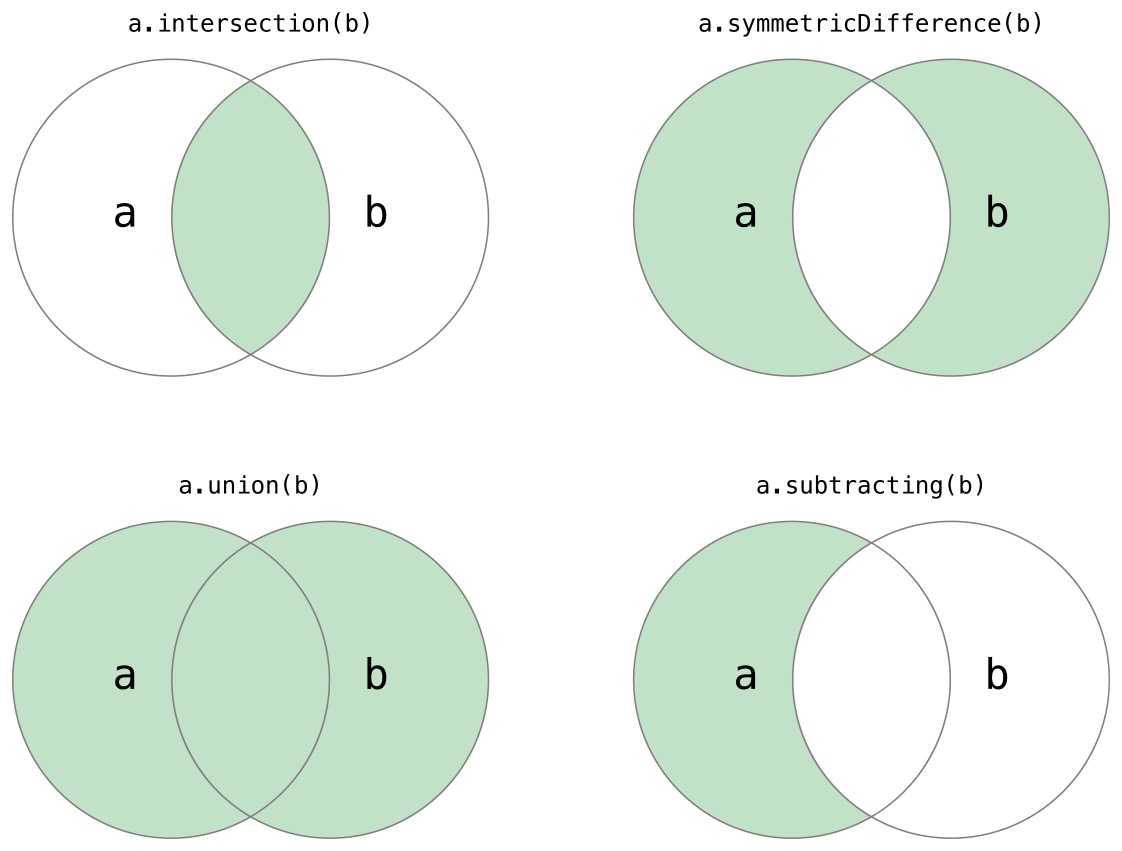
Set Membership and Equality
==判断两个set是否相等isSubset(of:)isSuperset(of:)判断包含另一个set的全部valueisStrictSubset(of:)isStrictSuperset(of:)subset/superset 但是不相等isDisjoint(with:)两个set没有相等的value
2. Dictionary
通过dictionary的keys或者values快速初始化数组
let keyArr = [String](dic.keys)
let valueArr = [String](dic.values)
Quiz
Q1: Sting 类型的 count 属性的时间复杂度是多少?Array呢?
String count 是 O(n), Array count 是 O(1)。 因为Swift 中 String 的 count 计算的是字符组合之后的长度。
var word = "cafe" // cafe,长度是 4
word += "\u{301}" // café,长度还是 4


留下评论